
Il caso studio del viadotto Alveo Vecchio
Emissioni acustiche per il rilevamento della rottura dei fili di precompressione
Autori: Bernardino Chiaia, Giulio Ventura, Marilisa Conte, Oscar Borla, Placido Migliorino
Rivista: STRADE & AUTOSTRADE N°5 Anno 2021
La sicurezza dei ponti in cemento armato precompresso post-teso e il monitoraggio nel tempo dell’acciaio di precompressione sono temi che hanno recentemente acquisito una grande attenzione sia dal punto di vista scientifico che della manutenzione e sorveglianza continua delle strutture. Le Emissioni Acustiche (EA) vengono utilizzate con successo da molti decenni in ambiti di tipo industriale, meccanico ed aeronautico, e sono un utile strumento per il controllo della progressione del danneggiamento di elementi strutturali o di aree particolarmente critiche di alcuni componenti.
Full-scale testing and analysis of 50-year old prestressed concrete bridge girders
Autori: F. Tondolo, D. Sabia, B. Chiaia, A. Quattrone, P. Savino (Department of Structural, Geotechnical and Building Engineering, Politecnico di Torino, Turin, Italy); F. Biondini, G. Rosati, M. Anghileri (Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy)
Capitolo di libro: Bridge Safety, Maintenance, Management, Life-Cycle, Resilience and Sustainability
1st Edition
The present research covers the full-scale loading tests conducted on 50-year old prestressed concrete girders. The beams were removed from an existing viaduct in Turin, Italy, and gave the possibility to setup a large experimental campaign as part of the research project named BRIDGE|50 (www.bridge50.org). The precast prestressed concrete beams have approximately 19.2 m span length and I-shaped cross section with 14 cm cast-in situ slab. For each specimen, static tests have carried out applying monotonic and cyclic loading profiles up to the ultimate load, measuring deflections, loads and strains in several positions. The results of the tests in terms of load-deflection responses and strains are reported for each beam investigated and compared each other. The experimental findings highlight the global structural response and the outcomes will define a reference for future studies aimed to assess the residual structural performance of existing bridges.

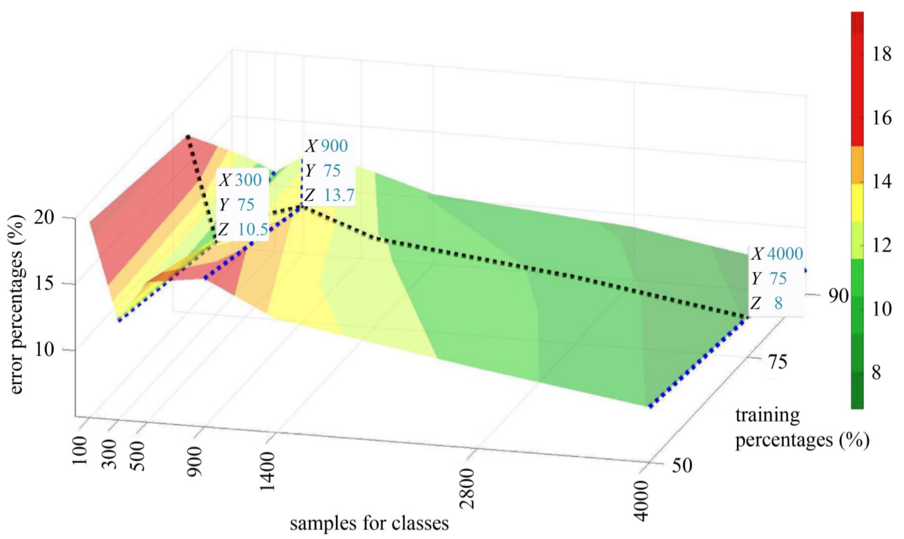
Deep convolutional neural network for multi-level non-invasive tunnel lining assessment
Autori: Bernardino CHIAIA, Giulia MARASCO , Salvatore AIELLO (Department of Structural, Geotechnical and Building Engineering, Polytechnic University of Turin, Torino 10129, Italy)
Rivista: Frontiers of Structural and Civil Engineering volume 16, pages214–223 (2022)
In recent years, great attention has focused on the development of automated procedures for infrastructures control. Many efforts have aimed at greater speed and reliability compared to traditional methods of assessing structural conditions. The paper proposes a multi-level strategy, designed and implemented on the basis of periodic structural monitoring oriented to a cost- and time-efficient tunnel control plan. Such strategy leverages the high capacity of convolutional neural networks to identify and classify potential critical situations. In a supervised learning framework, Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) profiles and the revealed structural phenomena have been used as input and output to train and test such networks. Image-based analysis and integrative investigations involving video-endoscopy, core drilling, jacking and pull-out testing have been exploited to define the structural conditions linked to GPR profiles and to create the database. The degree of detail and accuracy achieved in identifying a structural condition is high. As a result, this strategy appears of value to infrastructure managers who need to reduce the amount and invasiveness of testing, and thus also to reduce the time and costs associated with inspections made by highly specialized technicians.



